Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver, a vital organ that helps process nutrients, filter blood, and fight infections. When the liver becomes inflamed or damaged, its functions can be impaired, leading to serious health problems.
Causes of Hepatitis
Hepatitis can be caused by:
- Viral infections (most common)
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Toxins and certain medications
- Autoimmune diseases (when the immune system attacks the liver)
Types of Viral Hepatitis
There are several types, but the most common are:
1. Hepatitis A (HAV)
- Transmission: Through contaminated food or water, or close contact with an infected person.
- Severity: Usually short-term and doesn’t lead to chronic illness.
- Prevention: Vaccination, good hygiene, and safe food handling.
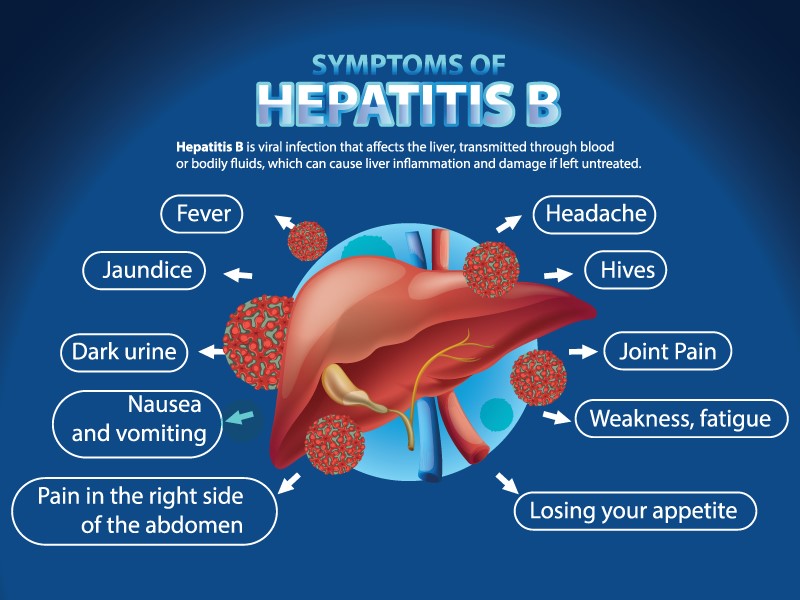
2. Hepatitis B (HBV)
- Transmission: Through contact with infected blood, unprotected sex, or from mother to baby at birth.
- Severity: Can be acute (short-term) or chronic (long-term). Chronic cases may lead to liver cirrhosis or cancer.
- Prevention: Vaccination, safe sex practices, avoiding sharing needles.
3. Hepatitis C (HCV)
- Transmission: Mainly through contact with infected blood (e.g., unsafe injections, transfusions with unscreened blood).
- Severity: Often becomes chronic and can cause long-term liver damage.
- Prevention: No vaccine yet, but avoiding risky blood exposure reduces chances.
4. Hepatitis D (HDV)
- Transmission: Occurs only in people already infected with hepatitis B.
- Severity: Can cause more severe illness than HBV alone.
- Prevention: Prevent HBV infection through vaccination.
5. Hepatitis E (HEV)
- Transmission: Through contaminated water or food.
- Severity: Usually acute and resolves on its own, but can be dangerous for pregnant women.
- Prevention: Good sanitation and safe drinking water.
Common Symptoms of Hepatitis
Some people may have no symptoms, especially in the early stages. When symptoms appear, they can include:
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Fever
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Dark urine
- Pale stools
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
Complications if Left Untreated
Chronic hepatitis can lead to:
- Liver cirrhosis (scarring)
- Liver failure
- Liver cancer
Prevention Tips
- Get vaccinated for Hepatitis A and B
- Practice good hygiene (wash hands regularly)
- Drink safe, clean water
- Avoid sharing needles, razors, or toothbrushes
- Practice safe sex (use condoms)
- Ensure blood for transfusion is screened
Treatment
- Hepatitis A & E: Usually resolve on their own; supportive care is given.
- Hepatitis B: Antiviral medicines for chronic cases.
- Hepatitis C: Highly effective antiviral medications can cure most cases.
- Hepatitis D: Managed by treating HBV infection.
✅ Key Takeaway:
Hepatitis is preventable in many cases, treatable in most, but can be deadly if ignored. Early detection, vaccination, and safe lifestyle practices are the best protection.